Nanomaterials constituent components that are smaller than 100nm in at
least one dimension. The study of controlling matter on
an
atomic
and molecular scale, nanotechnology, has the
potential to create new
materials and devices with a vast range of
applications in medicine,
electronics
and energy production. Nanotechnology has stirred up a
great amount of attention for improving disease
prevention, diagnosis, and treatment
[1].
Ordered or random nanotopographies can be synthesized by a number of fabrication techniques such
as electrospinning, phase separation, self-assembly
processes, thin film deposition, chemical vapor
deposition, chemical etching, nano-imprinting,
photolithography, and electron beam or nanosphere
lithographies.
Nano materials can be composed of metals,
ceramics, polymers, organic materials and composites.
They include nanoparticles, nanoclusters, nanocrystals,
nanotubes, nanofibers, nanowires, nanorods, nanofilms, etc
[2].
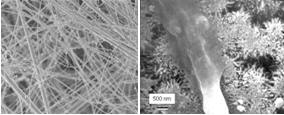
Nanomaterials hold a promise for bone, cartilage, vascular, neural and bladder tissue engineering
applications. Nanofibers can accurately simulate
the dimensions of natural entities, such as bone and
collagen. Superior physiochemical properties such as
mechanical, electrical, optical, catalytic and magnetic
properties can be generated by decreasing material size
into the nanoscale. As a result, nanomaterials have been
extensively investigated in a wide range of biomedical
applications, particularly regenerative medicine. Since
natural tissues are nanometer in dimension and cells
directly interact with and create nanostructured
extra-cellular matrices (ECM), the biomimetic features
and physiochemical properties of nanomaterials play a
critical role in stimulating cell growth and guiding
tissue regeneration
[3].
The ability to precisely control and integrate inorganic and organic nanostructures holds the promise of a
completely new generation of advanced composites and
applications in the medical field.
References
[1]
OV Salata.
Applications of nanoparticles in biology and medicine.
Journal of Nanobiotechnology (2004),
vol.
2
[2]
Alan S. Edelstein,
Robert C. Cammarata. Nanomaterials:
synthesis, properties, and applications.
(1996)
[3]
Lijie Zhang, Thomas J. Webster. Nanotechnology and nanomaterials:
Promises for improved tissue regeneration.
Nano Today (2009), vol. 4, pp.66—8


