
The basic principle of IVUS is utilizing a piezoelectric material generate a beam of acoustic wave from a catheter inside the lumen of an arterial vessel, and analyze the reflected wave to reconstruct a 2D or 3D map of vessel wall. IVUS consist of a catheter with piezoelectric transducer at its tip and an electronic system to reconstruct the retrieved acoustic signal to image.

ˇ@
ˇ@
ˇ@
ˇ@
ˇ@
ˇ@
ˇ@
ˇ@
The operation frequency of the generated acoustic waves is around 12.MHz to 50MHz, and the acoustic waves are thus called ˇ§ultrasound.ˇ¨ The optimal frequency is determined by the size of vessel. This is because the wavelength of ultrasound is direct relate to frequency, where the acoustic velocity is constant in one media, and it determines the resolution and sensitivity of ultrasound beam. Thus, the optimal frequency for larger vessel is range from 12.5 MHz to 20MHz, and the range for smaller vessel is up to 30 MHz to 40 MHz.
ˇ@
How IVUS work?
The catheter with acoustic transducer is advanced over the wire inside the arterial vessel, where most of cases are coronary artery, and it is pushed to the distal position of the investigating vessel segment. A cross-sectional scan of vessel wall is captured by acoustic transducers, and a longitudinal scan is made by a slowly pull back of catheter (0.5 to 1 mm/s) from distal to proximal segment of vessel. These two functions are operated simultaneously and a 3D image of vessel wall can be reconstructed. A motorized pulled back system with a predetermined pulling speed is essential to make the image repeatable and allow user to re-access a particular portion of the vessel wall.
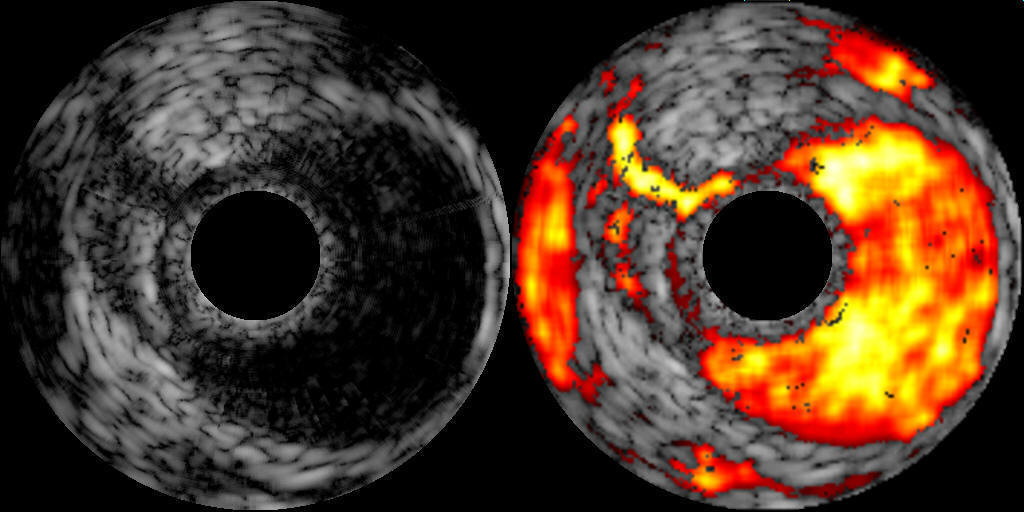
The following is an image of taking from IVUS system.
ˇ@
ˇ@
ˇ@
ˇ@
ˇ@
The following is a link to a demo video of Galaxy²™ IVUS Imaging System, which can give us an idea of how IVUS work.
ˇ@
ˇ@
Pinciples
of IVUS ˇG![]() Piezoelctric
effect
Piezoelctric
effect
![]() Mechanically rotating transducer (Mechanical system)
Mechanically rotating transducer (Mechanical system)
![]() Electrically
switched multi-element array system (Electrical system)
Electrically
switched multi-element array system (Electrical system)
ˇ@
ˇ@

