![]()

¡@
¡@
Acoustic wave is a disturbed pressure that propagating through a certain kind of media that carrying mechanical energy with it. The medium is simply the material that the disturbance is moving, and the mechanical energy is thus carried through this medium from one location to another. The type of wave of acoustic waves utilized in IVUS is longitudinal wave, where the vibration of particles is parallel to the propagating direction of energy. A beam of longitudinal acoustic wave is generated by the compression and rarefaction pressure generated by the piezoelectric transducer. A sequence of high pressure and low pressure is induced by the piezoelectric transducer, and a beam of acoustic wave is generated in the lumen of the blood vessel.
¡@
¡@
¡@
¡@
¡@
¡@
¡@
¡@
¡@
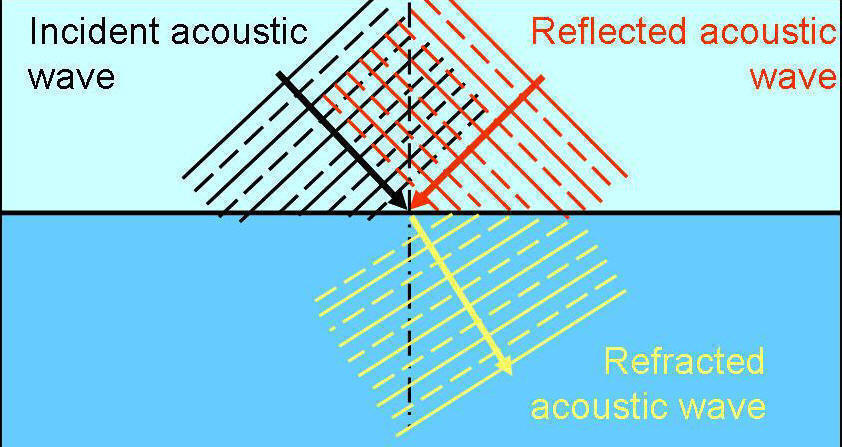
The blood and tissues of vessels provide different layers for acoustic wave to travel. Because the velocities different for different material, acoustic waves will reflected and refracted at these interfaces. This is because the acoustic impedance is different for different layers. Thus, the amplitude and phase of the reflected and refracted acoustic will carry material and geometrical information for each layer. By decoding these reflected signals, IVUS can reconstruct a 2D or 3D image of blood vessel walls and provide a golden tool for doctor to diagnose vascular diseases.
The variations of acoustic impedance are relied on the different compositions of blood and different layers of blood vessel walls. This is called echogenecity of media, where depends on the amount of smooth muscles, collagen and elastin. Collagen and elastin are strongly echoreflective, which is about 1000 times larger than that of smooth muscle. Then IVUS can distinguish intima, internal lamina, external elastic lamina, and adventitia (Link to Classic IVUS image), and different types of blood vessels, plaques and lesions (Link to clinical applications)
¡@

