Contents
1. Introduction
2. Neurosurgical Interventions
3. Clinical Applications of DTI
1. Introduciton
DTI has been used in a wide spectrum of applications. The primary reason is that water diffusion is highly sensitive to differences in the microstructure of cellular membranes in tissues. Increase in the average spacing in tissues will increase the apparent diffusivity, whereas smaller spaces will lead to a lower apparent diffusivity. This sensitivity makes DTI a powerful method in detecting microscopic tissue properties. Nevertheless, the diffusion tensor is a complex construct and should be examined with care.
2. Neurosurgical Interventions
The
major
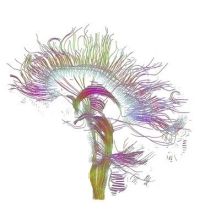
application of DTI in neurosurgical intervention is mapping of white
matter (WM) prior to surgery
[1]. Mapping of WM assists
the neurosurgeon with localization of critical white matter pathways,
that need
to be preserved during surgery. The pathways may be visualized as RGB
colormaps or via tractography (see Fig. 3 and Fig. 4 in the part about DTI).
A recent
study published by Powell at al. [2], suggests that
tractography could
also
predict visual field deficits that occur during the resection of the
temporal
lope.
Take a look at this video showing BrainLAB's software (BrainLAB iPlan® FiberTracking) for neurosurgical planning based on DTI.
(►
3. Clinical Applicaitons of DTI
Ischemic stroke
The clinical diagnosis and characterization of acute ischemic lesions in the CNS is by far the most common clinical application of DTI. In the acute phase of brain ischemia, the MD significantly decreases in the lesion [5]. Resent studies have also shown that the FA appears to increase in acute lesions and decrease below baseline levels in the chronic phase [6].
Neoplasia
The second most common clinical application of DTI is possibly for the characterization of white matter in patients with brain tumors. This work focuses on using DTI maps and tractography to help localize WM fiber tracts that are important for such critical functions as motion, language, and vision. Based on this information the neurosurgeon can plan surgical procedures that will minimize injury to critical tracts, such as the corticospinal tract [7].