Multilayer Nanoencapsulation
---------- New Approach for Immune Protection of Human Pancreatic Islets
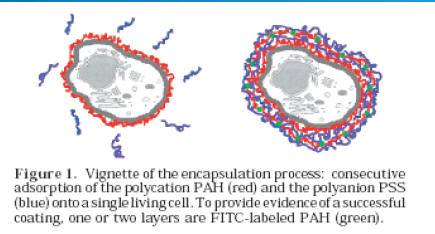
Immune protection of artificial tissue by means of microencapsulation is a very ambitious new approach to avoid lifelong immune suppression especially in the case of juvenile recipients (type 1 diabetes). The aim is to transplant islets with a minimum or no immune suppression. Great progress has been achieved since the conception of this idea. Here, a new multilayered nanocapsule as a more flexible encapsulation for islets is introduced. Interactions with cells adhering on the multilayered surface are numerous and give evidence of how powerful this method is. Several groups modulate surfaces in a way that they induce or facilitate the binding of different cell types. The number of polyelectrolytes which can be used and combined to prepare multilayers is endless.
the present study shows that a new multilayered nanocapsule is a more flexible encapsulation for islets Interactions with cells adhering on the multilayered surface are numerous and give evidence of how powerful this method is. The idea of applying multilayers via lbl directly to the Langerhans islets was fascinating.
Designed by Shan Yang