|
|
| |
 In-vivo Study of Imagify
In-vivo Study of Imagify
|
|
|
|
| |
The objectives of this study were (1) to assess whether 2-dimensional (2D) MCE after intravenous bolus administration of AI-700 can detect myocardial perfusion defects; and (2) to examine whether 3D MCE acquired after a single bolus of AI-700 can accurately quantify the size of myocardial perfusion defect or "area at risk of infarction" compared with nuclear imaging and predict the infarct myocardial mass after a prolonged coronary artery occlusion without reperfusion, compared with anatomic triphenyl tetrazolium chloride (TTC) staining.
|
|
|
|
| |
The group performed MCE in a canine model of acute ischemia and infarction induced by coronary occlusion in 14 mongrel dogs (23 - 29 kg). Each dog was sedated with intramuscular acepromazine and anesthetized with intravenous thiopental. Then the dog was intubated, ventilated with a volume cycle respirator, and kept anesthetized with isoflurane. A 7F catheter was placed in a femoral artery for blood pressure monitoring and another one in a femoral vein for fluid and contrast administration. The chest was opened by median thoracotomy to isolate and occlude a main branch of the coronary artery (anterior descending coronary artery in 12 dogs and circumflex coronary artery in 2 dogs). Then the chest was closed. Intravenous lidocaine was given before coronary occlusion and continued throughout the study to prevent ventricular fibrillation. Arterial blood pressure, oxygen saturation, and ECG were monitored throughout the study.
|
|
|
|
| |
A commercially available ultrasound unit, either ATL HDI 5000 (Advanced Technology Laboratories, Bothell, Wash) or HP SONOS 5500 (Agilent Technologies, Andover, Mass) was used for echocardiographic imaging. The mechanical index, used as a surrogate for ultrasound power output, was 1.0 to 1.1 for gray scale harmonic imaging and 0.9 to 1.3 for power Doppler imaging. The trigger delay from the R wave on the electrocardiogram and the color gain were carefully adjusted for power Doppler imaging at baseline to exclude artifacts and Doppler signals produced by wall motion. The pulse repetitive frequency used for power Doppler imaging was 1500 Hz (ATL) or 1600 Hz (HP).
|
|
|
|
| |
2D MCE images were acquired in a right parasternal window with the chest closed and the dog placed in a right decubitus position. After baseline images of multiple short-axis views (at the midpapillary muscle, near-apex and high-papillary muscle levels) and a long-axis view of the left ventricle (LV) were obtained, AI-700 was administered intravenously as a slow bolus (4 mg/kg over a period of about 45 seconds), followed by a 2-mL sterile water flush injected over 20 seconds. Contrast enhanced images were obtained using both gray scale second harmonic imaging mode and power Doppler imaging mode, each after a single bolus of AI-700. At least 30 minutes were allowed between 2 imaging sessions to allow for contrast agent clearance from the previous injection. Images in each view were obtained in both continuous and triggered (1:1 and 1:4) fashion. Triggered images were acquired at end systole. All imaging data were recorded onto super VHS videotapes for later analysis.
|
|
|
|
| |
After completion of 2D MCE imaging, the chest was reopened for precordial 3D MCE data acquisition using triggered (1:1, end systole) second harmonic imaging mode. After a separate bolus of AI-700, the MCE images from the ultrasound machine were transferred and collected by a stand alone 3D processor (TomTec, Echo Scan, Munich, Germany) in a rotational mode at 3-degree intervals. The probe was encased in a rotational device held by a mechanical arm. The rotation of the probe, thus the imaging plane, was controlled automatically by the 3D processor gated to ECG and respiration. The 3D data were calibrated, processed and stored onto M-mode disks for offline analysis.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
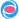
Fig. 10 Anterior myocardial perfusion defect
|
|
|
|
|
|
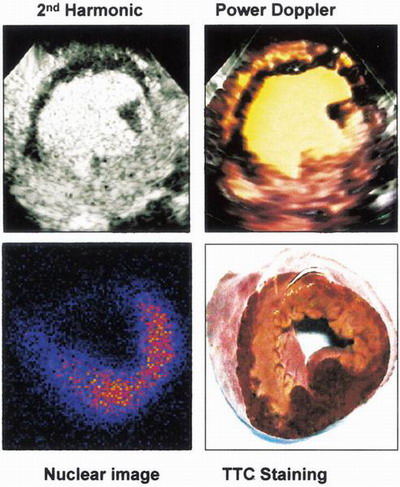
Fig. 11 Posterior perfusion defect
|
|
|
|
|
|
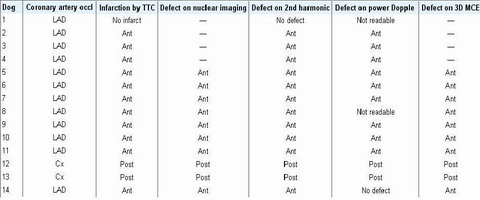
Table. 2 Demographic localization of coronary artery occlusion, myocardial infarction, and perfusion defect. (Occl, Occlusion; TTC, triphenyl tetrazolium chloride; MCE, myocardial contrast echocardiography; LAD, left anterior descending coronary artery; Ant, anterior wall; Cx, left circumflex coronary artery; Post posterior wall; --, not performed.)
|
|
|
| |
This experimental study demonstrated that a single intravenous bolus of AI-700 could enhance the myocardium for 3 to 4 minutes during not only triggered, but also continuous second harmonic imaging and during triggered power Doppler imaging in closed-chest dogs. It was possible to image the heart in multiple views to assess the myocardial perfusion abnormalities of all coronary territories after a simple, single bolus injection of AI-700. A single bolus injection of AI-700 also permitted enough time of myocardial enhancement for 3D MCE data acquisition and to allow for more accurate quantitative analysis of perfusion defect size and perfusion defect mass.
|
|
|
|
|