Bubble Ultrasound-Guided Biopsy/ Surgery
BME 240
| |
| Home |
| Background |
| Applications |
| Future |
| References |
| Applications |
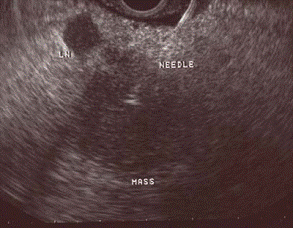
EUG-FNA One paper presented by the Isam Eltoum group at University of Alabama, performed EUS-FNA on 547 resulting in 95% sensitivity, 92% specificity, and overall accuracy of 94.1%. There was 414 true positive diagnosed with EUG-FNA, of which 138 were further explored. These numbers reveal that EUG-FNA is a safe and accurate method for diagnosing pancreatic cancer. Preoperative counseling would be greatly enhanced by making this procedure common practice, thereby avoiding unnecessary biopsies and surgeries on unresectable disease. [11] The actual procedure of EUG-FNA involves passing an 18 to 22 gauge metal needle through the biopsy port of a echoendoscope, guided by real-time ultrasound imaging, and into the suspected mass, associated lymph node, liver metastasis, or fluid collection. The needle is then move in and out of the mass 5 to 10 times with varying degrees of suction. The specimen is later deposited on cytology slides to be fixed and stained for cytopathologic examination [12]. Figure 8 shows an ultrasound image of a EUG-FNA being performed on a mass in the pancreas. [11] From its beginning, the needle technology of the EUG-FNA echoendoscope has made significant advances resulting in at least three manufacturers of effective disposable and semi-disposable EUG-FNA needles. New innovative devices such as spring activated needles are helping penetrate firm lesions and cutting needles are providing small cores of tissue to try and perhaps improve diagnostic capabilities |
|