E-mail:
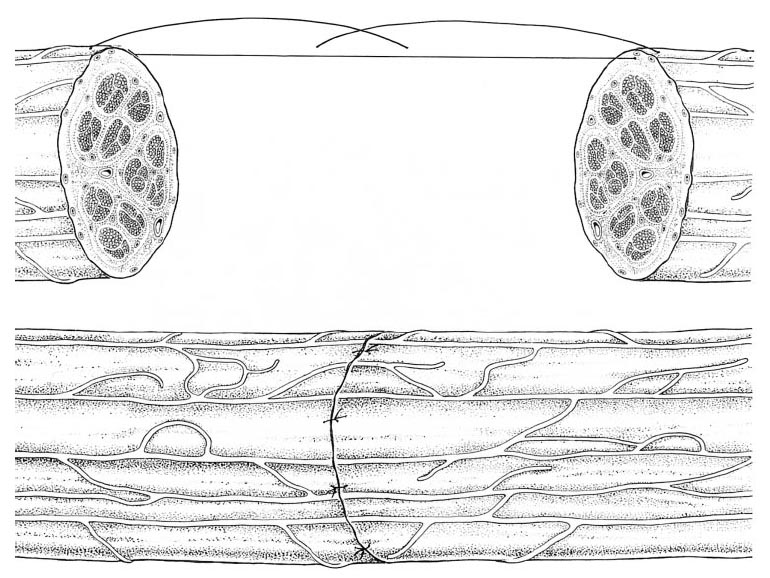
The nerve defects, such as severed nerves, will cause a loss of function and require microsurgery. Usually, suturing or nerve grafts are employed depending on the injury distance between the proximal and distal nerve segments. The purpose of suturing two nerve segments is to facilitate proper alignment between the fascicles, mimicking the native nerve before damage in order to preserve function. Figure 1 shows two examples of direct nerve suturing.2 This procedure is only used when the injury distance is small, because of biomechanics. Non-normal physiological tension created as a result of suturing will negatively affect the nerve trunk. As a result, larger transected distances require a nerve graft.
 |
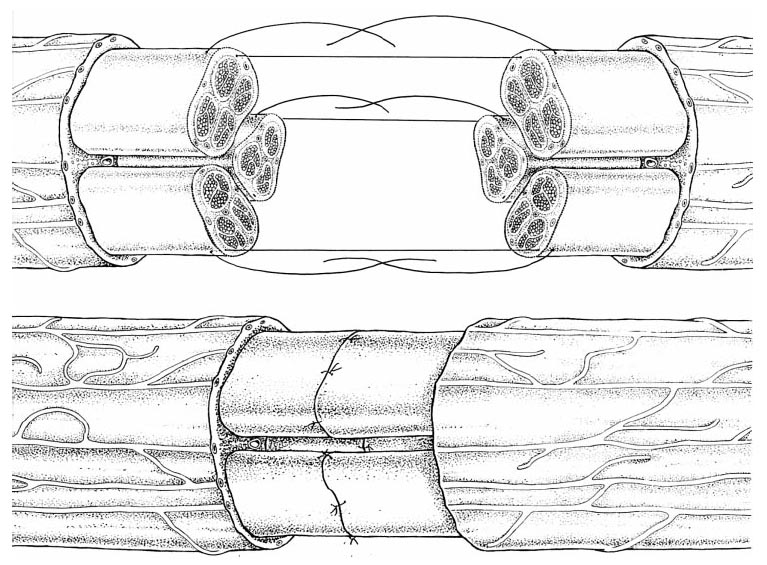 |
Figure 1a. Epineural suturing.2 Figure 1b. Group fascicular suturing.2
To repair the larger gaps in distance, the common treatment method is replacement via autologous nerve grafts; however, other techniques include using allografts or nerve guidance channels. Nerve grafts can come in various forms, including nerves, veins, muscles, and even arteries.4 The current gold standard for treating patients with peripheral nerve injury is using autologous nerve grafts. By using an autologous nerve graft, there is no immune rejection. In addition, this can help facilitate proper axon regeneration by using a healthy nerve as a substrate. However, acquiring an autologous nerve graft requires an additional surgery to dissect a nerve, which usually is from sural or saphenous nerve. By losing function at this site, the patient hopes to regenerate some function at the injured site, but there is no guarantee. This requires multiple surgical procedures for something not guaranteed.
Allografts and nerve guidance channels offer excellent options to autologous nerve grafts. Allografts can be easily harvested; however, reproducibility and immune response are major concerns. Nerve guidance channels are the optimal treatment method, as they are easily reproducible and designed to elicit no immune response. However, many research groups are working on designing the optimal conditions necessary to produce results similar to, if not better, then autologous nerve grafts.3,4