Introduction

TOTAL ARTIFICIAL HEARTS
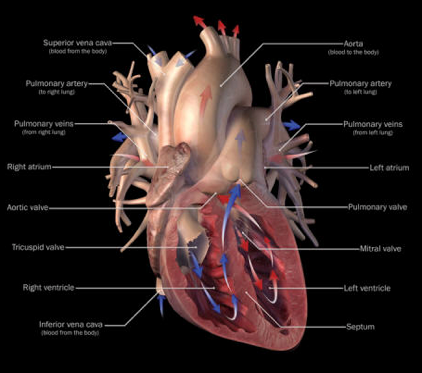
The heart is the organ responsible for pumping blood through the circulatory system. The organ itself is divided into four chambers consisting of two superior atria and two inferior ventricles, where blood flows into the atria and out the ventricles. The tricuspid, pulmonary, mitral, and aortic valves are the four valves, which allow for the unidirectional flow of blood when the heart beats by preventing backwards flow. Blood flow is a result of the difference in pressure across these valves which causes them to open. The heart pumps blood due to a electrical impulse governed by the sioatrial (SA) node. Deoxygenated blood from the body flows into the right atrium, where it goes into the tricuspid valve and then into the right ventricle. Blood is then pumped into the lungs making it oxygenated. This oxygen rich blood now flows into the left atrium of the heart through the mitral valve where it goes into the left ventricle. Blood is then pumped through the aortic valve to the aorta and back out to the body. This process is cycled over and over.
The HUman Heart