The Aortic Valve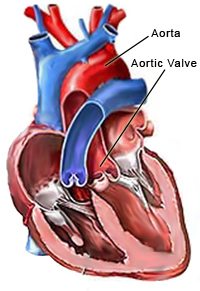
The aortic valve is one of four valves in the human heart, and plays an important role ensuring that blood pumped from the powerful left ventricle flows forward to the rest of the body. Problems with the aortic valve can be divided into two broad categories, known as aortic regurgitation and aortic stenosis. If the aortic valve becomes severely diseased,aortic valve replacement surgery may be required.A normal aortic valve opens during contraction of the heart and closes during the relaxation period. This ensures that blood flows forward to the rest of the body and not back into the heart. If the valve leaks when it should be closed, aortic regurgitation is present. This causes the heart to work harder to pump extra blood to overcome the volume load it faces. If the valve becomes narrowed and obstructed (usually due to calcification), aortic stenosis is present. Both aortic stenosis and aortic regurgitation decrease the amount of blood that can be pumped from the heart to the body and lead to enlargement of the heart. Some patients may remain asymptomatic, while others experience increased fatigue, shortness of breath, swelling of the legs and possibly fainting episodes.
Aortic Valve Disease
Aortic Valve disease can be a consequence of problems that have been present since birth (congenital heart defects) and problems that occur due to aging and wear and tear of the valve. The most common congenital heart problem affecting the aortic valve is known as a bicuspid aortic valve. A bicuspid aortic valve has two "cusps" as opposed to the usual three cusps seen in a normal valve. This congenital heart problem occurs in around 2% of the general population.The most common aortic valve problem associated with aging is aortic valve stenosis. As the valve ages, a person may get a buildup of calcification and fibrosis on the valve. This limits the ability of the valve to function properly and decreases the amount of blood flow to the brain and the rest of the body. The valve usually needs to be replaced in this condition.