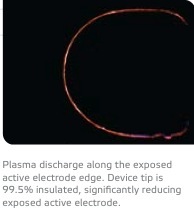
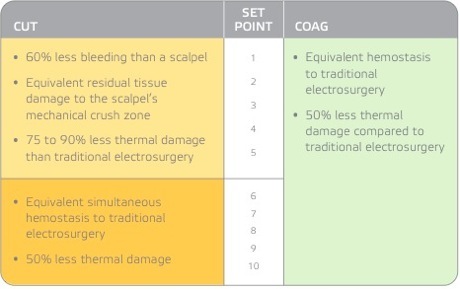
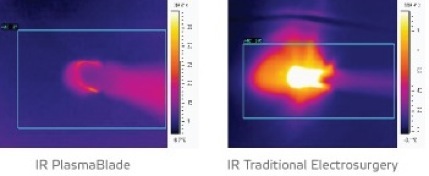
The Peak Surgery System provides for a unique balance between precision cutting and bleeding control. The technology enables a surgeon to:
-
-Cut precisely through any type of tissue (including muscle)
-
-Fine tune the amount of bleeding control to the target tissue; effectively minimizing thermal damage.
-
-Operate at 50% lower temperatures than traditional electrosurgery technology, going as low as 50º C.
-
-Utilize about 50% the amount of watts than traditional electrosurgery technology.
-
-Maintain performance in both a wet and dry field.
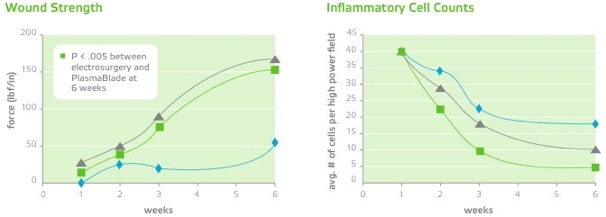
Studies have revealed:
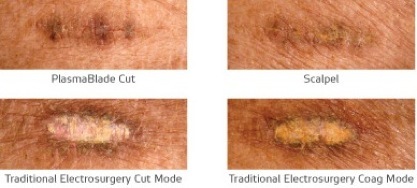
-Reduced scarring
-Reduced inflammation
-Stronger surgical incision wound healing.
-Increased cutting speed and precision.
-Significantly reduced eschar build up
-Little to no surgical smoke while in the cut mode.
-Less cutting force required than a slapel and traditional electrosurgery.