In the future, contrast enhanced ultrasound is thought to emerge not only as a diagnostic tool, but also for therapeutic purposes. Some of the areas where
it has wide application are as follows:
- Inflammation
In inflammatory diseases, the inflamed blood vessels specifically express certain receptors like VCAM-1, ICAM-1, E-selectin. If microbubbles are
targeted with ligands that bind these molecules, they can be used in contrast echocardiography to detect the onset of inflammation. Early detection
allows the design of better treatments.
- Cancer detection
Cancer cells also express a specific set of receptors, mainly receptors that encourage angiogenesis, or the growth of new blood vessels. If
microbubbles are targeted with ligands that bind receptors like VEGF, they can non-invasively and specifically identify areas of cancers.
- Gene Delivery
Vector DNA can be conjugated to the microbubbles. Microbubbles can be targeted with ligands that bind to receptors expressed by the cell type of
interest. When the targeted microbubble accumulates at the cell surface with its DNA payload, ultrasound can be used to burst the microbubble. The
force associated with the bursting may temporarily permeablize surrounding tissues and allow the DNA to more easily enter the cells.
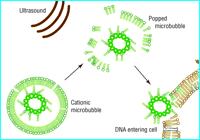
The figure alongside shows gene delivery using ultrasound and microbubbles. The presence of gas in the gene-filled
microbubble allows ultrasound energy to pop the microbubble. An energetic wave is then created whch allows the genetic
material to enter surrounding cells.
- Drug Delivery
Drugs can be incorporated into the microbubble’s lipid shell. The microbubble’s large size relative to other drug delivery vehicles like liposomes may
allow a greater amount of drug to be delivered per vehicle. By targeting the drug-loaded microbubble with ligands that bind to a specific cell type,
microbubble will not only deliver the drug specifically, but can also provide verification that the drug is delivered if the area is imaged using
ultrasound.
Other Anticipated developments are listed below:
- Robust methods for detecting and measuring microcirculatory flow, allowing quantification of regional ischaemia in the myocardium and other organs.
- Routine use of microbubbles to enhance imaging of the liver parenchyma, improving accuracy of ultrasonographic assessment and staging of cancer.
- Microbubble based methods of non-invasive clot lysis.