Diagnose the hereditary disease and viral infection at home:DNA Microarray
(Genome Chip)
Intro
It is widely believed that several hereditary diseases are correlated to specific genome sequence expression. Traditional methods in molecular biology generally work on a "one gene in one experiment" basis, which limit the throughput and delay the discovery of the corelations between the genome epression and hereditary diseases. In the past several years, a new technology, called DNA microarray, has attracted tremendous interests among biologists, especially for the scientist working in the human genome sequence project. This technology promises to monitor the whole genome on a single chip so that researchers can have a better picture of the interactions among thousands of genes simultaneously.
Principle
The underlining principle of DNA microarray is the base-pairing of DNA structure.
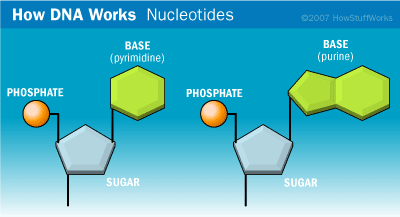
DNA microarray
An DNA microarray is an orderly arrangement of samples. (As figure below). It provides a medium for matching known and unknown DNA samples based on base-pairing rules and automating the process of identifying the unknowns. In general, arrays are described as macroarrays or microarrays, the difference being the size of the sample spots. Macroarrays contain sample spot sizes of about 300 microns or larger and can be easily imaged by existing gel and blot scanners. The sample spot sizes in microarray are typically less than 200 microns in diameter and these arrays usually contains thousands of spots. Microarrays require specialized robotics and imaging equipment that generally are not commercially available as a complete system.
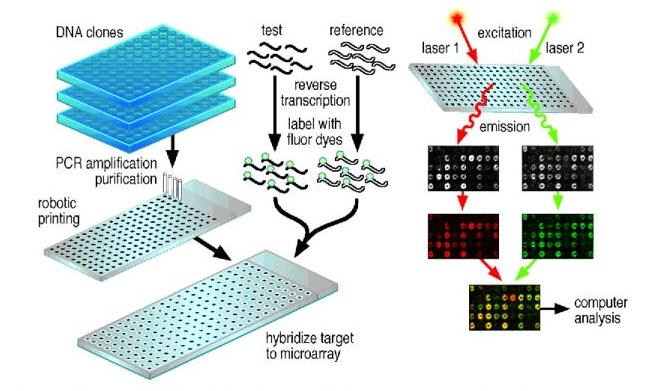
Major functions and applicaiton
There are two major application forms for the DNA microarray technology, which could be utilized to diagnosis the disease.
-
Identification of sequence (gene / gene mutation): This applicaiton can be used to identify the genome expression for hereditary diseases first, and then map out which genome expression would directly related to certain hereditary diseases. Once the sequence for different hereditary diseases was clarified, the commercial available diagnostic biochip for the hereditary diseases would become possible.
-
Determination of expression level (abundance) of genes: Durign the viral infection, the viral genome would upregulate the protein expression in the host level so that it would help to produce the DNA polymerase for viral DNA systhesis. As the virus start to duplicate the virus particle, the viral genome would show significant abnormal expression. By using the DNA array, it could also be detect while the infection is in the early stage.
Commercial available product
Affymetrix, Inc. owns owns a registered trademark, GeneChip®, which refers to its high density, oligonucleotide-based DNA arrays. More recently, it was refered as the term "genome chip", indicating that this technology is meant to monitor the whole genome on a single chip. GenomeChip would also include the increasingly important and feasible protein chip technology.


